Every app collects user data names, emails, payment details, locations, and more. But not every app protects this data properly. If this information falls into the wrong hands, it can lead to severe problems such as identity theft or data leaks.
That’s why developers use data anonymization. It’s a process where personal details are removed or changed so that the data can’t be linked back to a specific person. This allows companies to use data for analysis, research, or testing without risking user privacy.
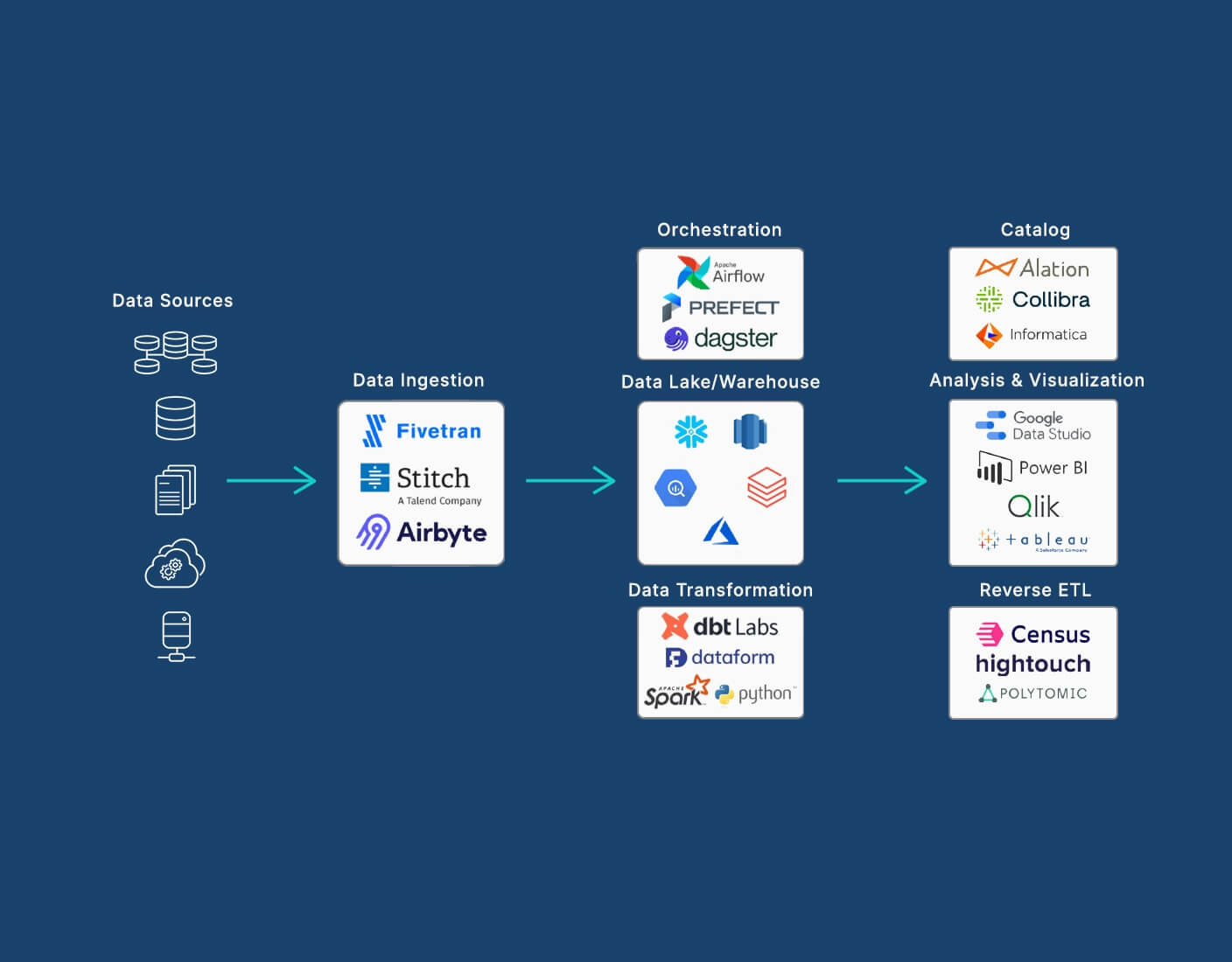
For full stack developers, building a complete data anonymization pipeline means handling both the backend and frontend parts of the process. It involves collecting the data, processing it, anonymizing it, and then storing or displaying it safely. That’s why many full stack developer classes now include lessons on data privacy and anonymization as part of their core topics.
In this blog, we’ll walk through how to build a data anonymization pipeline using a full stack approach. We’ll explain how to collect, anonymize, and manage data across the frontend, backend, and database in the simplest way possible.
What is Data Anonymization?
Data anonymization is the process of hiding or removing personal information from a data set. This can be done by:
- Masking: replacing real names with fake ones.
- Generalizing: changing exact ages into age groups.
- Encrypting: turning data into code that can’t be read without a key.
- Removing: deleting personal details completely.
The goal is to protect people’s identities while still allowing data to be used for analysis or testing.
For example, instead of showing “John Smith, 35, john@example.com,” you could show “User123, 30-40, hidden@example.com.”
This way, you can study the data but keep the user’s identity safe.
Why Use a Full Stack Approach?
A full stack approach means working on both the backend and frontend of an app. In a data anonymization pipeline, this is important because:
- The frontend collects user input (names, emails, etc.)
- The backend handles logic and processes the data
- The database stores the data securely
- Sometimes, the frontend displays data after anonymization
If all these parts are not handled carefully, user data can be exposed. A full stack developer needs to make sure data is protected at every step.
Step-by-Step Guide to a Full Stack Data Anonymization Pipeline
Let’s break down the process into simple steps.
Step 1: Collecting Data (Frontend)
The first part is collecting data from users. This usually happens through forms in a web or mobile app.
For example, a sign-up form might collect:
- Full name
- Email address
- Age
- Location
The frontend should:
- Validate the data (check for errors)
- Use HTTPS to encrypt data during transfer
- Avoid storing sensitive data in browser storage like localStorage
Step 2: Sending Data to the Server (API Layer)
Once the data is collected, it’s sent to the backend using APIs. This is done using tools like fetch, Axios, or built-in browser methods.
Always use POST requests for sensitive data, and avoid logging raw data in the browser console.
At this point, the data is still in its original form. The next step is to process and anonymize it.
Step 3: Anonymizing Data on the Server (Backend)
The backend is where the anonymization happens. This part depends on the programming language and framework you’re using Node.js, Python, Java, etc.
Here are some common anonymization techniques you can implement:
- Replace names with random strings: “John Smith” becomes “UserA45”
- Mask emails: “john@example.com” becomes “jo***@example.com”
- Generalize age: “34” becomes “30-40”
- Remove sensitive fields: delete full addresses, phone numbers, etc.
You can also use libraries or write custom functions to automate this.
After anonymization, the data can be saved in the database for further use, such as analytics or testing.
Many students who attend full stack developer classes get hands-on practice in setting up these backend pipelines, especially as more companies focus on data compliance.
Step 4: Storing Anonymized Data (Database)
Once the data is anonymized, it needs to be saved securely.
Use a reliable database system like PostgreSQL, MongoDB, or MySQL. Make sure:
- Sensitive fields are encrypted if needed
- Access is limited to authorized users
- Logs do not contain raw personal data
You can also store anonymized data in separate tables or collections to avoid mixing it with original data.
Always test your storage to make sure the data is properly anonymized and cannot be reverse-engineered.
Step 5: Displaying or Sharing Data (Frontend or API)
Sometimes, you need to show anonymized data back to the user or another system. This might be for dashboards, reports, or analytics tools.
Here, the frontend should:
- Only fetch the data it needs
- Never show real names, emails, or any personal detail
- Use charts or summaries instead of raw data
For example, instead of showing individual ages, show the average age of users.
If the data is shared through an API, make sure the output is also anonymized. Always test the final results from the user’s perspective to check for any leaks.
Security and Compliance
Data anonymization is not just a technical issue it’s also a legal one. Many regions have strict privacy laws like:
- GDPR (Europe)
- CCPA (California)
- HIPAA (for healthcare in the U.S.)
These laws require that personal data is protected and only used with consent.
As a full stack developer, you must understand the basic rules of data privacy and follow best practices. If your app deals with user data, anonymization should be a key part of your design.
You can also include logging and monitoring to track how data is processed and to spot any problems early.
Testing and Verification
An important step in the pipeline is testing. After you anonymize data:
- Double-check that all personal info is removed
- Try reverse-engineering it (can you guess the original user?)
- Get feedback from your team or users
If possible, use automated tests to scan for common personal data like names, emails, or addresses in your database or frontend views.
Testing is a good habit that helps prevent leaks and keeps your app secure.
Real-World Example
Let’s say you’re building a health tracking app. Users enter personal data like their name, age, and medical condition.
You want to use this data for research, but you must protect user privacy.
Your full stack pipeline might look like this:
- User enters their info on a form.
- The frontend sends the data to the server.
- The backend replaces names with random codes, generalizes age, and removes the exact condition name.
- The anonymized data is saved in a research database.
- A dashboard shows average health stats, not individual records.
Using this setup, you get useful data without exposing anyone’s personal information.
Projects like these are common in a full stack course, where students are asked to build apps that follow privacy rules and include safe data handling features.
Conclusion
Data anonymization is a key part of building modern apps. As more users become conscious of privacy issues, it’s the developer’s job to protect their data at every step.
Using a full stack approach means you manage how data is collected, processed, and stored from end to end. You can make sure the data is safe on the frontend, backend, and in the database.
Learning how to build anonymization pipelines will not only make you a better developer but also help you build trust with your users and clients.
If you’re learning web development in a full stack course, try creating a small anonymization project on your own. Even a simple one will teach you valuable lessons about data privacy, backend design, and secure coding.
Data is powerful but only when it’s handled with care.
Business Name: ExcelR – Full Stack Developer And Business Analyst Course in Bangalore
Address: 10, 3rd floor, Safeway Plaza, 27th Main Rd, Old Madiwala, Jay Bheema Nagar, 1st Stage, BTM 1st Stage, Bengaluru, Karnataka 560068
Phone: 7353006061
Business Email: enquiry@excelr.com